

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...
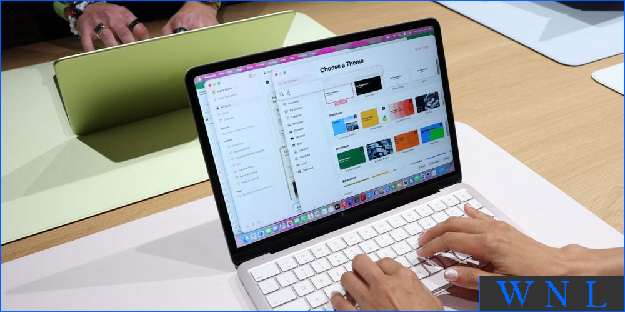
Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Introducing the better work project...

What's Shaping the K-Shaped Economy: Spendin...

Watch out, prediction markets. The 'super ap...

Atlassian to Cut 1,600 Jobs to Focus on AI, ...

Exec of laptop maker says Apple's budget Mac...

Blue Owl keeps chasing AI infrastructure dea...

China rushed to use OpenClaw. Now, some stre...

Oil spikes are pushing airlines to hike tick...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

Remote Monitoring App (Spy App) | 12-March-2...

SmartSync Data Sync App (Spy App) | 12-March...